Haitian immigrants grapple with uncertainty as TPS end date looms
Share
Explore Our Galleries
Breaking News!
Today's news and culture by Black and other reporters in the Black and mainstream media.
Ways to Support ABHM?
By Fredlyn Pierre Louis, NBC
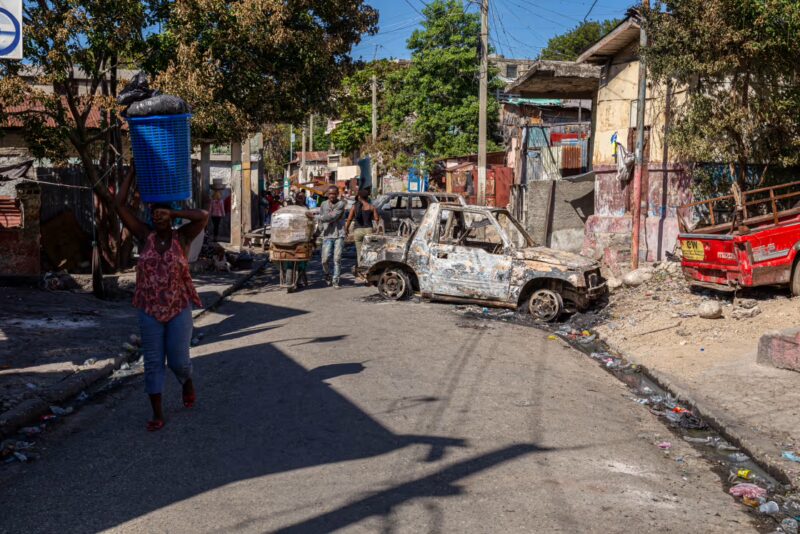
The same day Geslain Luma, a 29-year-old Haitian immigrant, learned he was granted temporary protected status to remain in the United States was the same day President Donald Trump announced plans to cut the program short.
Figuring out his future with “the end of TPS gives me a headache,” Luma said.
For more than 15 years, TPS has allowed thousands of Haitians to work legally in the U.S. and avoid deportation while their homeland grapples with political instability, gang violence and economic hardship.
Since the assassination of President Jovenel Moïse in 2021, armed gangs have gained control over much of Port-au-Prince, creating a power vacuum that has made governing a challenge and fueled further violence, homelessness and starvation. More than 5,600 people were killed and 1,400 were kidnapped amid gang conflicts last year, according to the United Nations. The violence has rendered 1 million people homeless in Haiti, forcing many into makeshift shelters and exacerbating the country’s economic challenges.
But with the Trump administration’s decision to end TPS by August 2025, an estimated 500,000 Haitian immigrants living in the U.S. face an uncertain future, forced to decide whether to stay and fight for legal status or prepare for a return to a country in crisis.
Learn about the Haitian communities in the US.
Discover more about the crisis in Haiti or Black history.









Comments Are Welcome
Note: We moderate submissions in order to create a space for meaningful dialogue, a space where museum visitors – adults and youth –– can exchange informed, thoughtful, and relevant comments that add value to our exhibits.
Racial slurs, personal attacks, obscenity, profanity, and SHOUTING do not meet the above standard. Such comments are posted in the exhibit Hateful Speech. Commercial promotions, impersonations, and incoherent comments likewise fail to meet our goals, so will not be posted. Submissions longer than 120 words will be shortened.
See our full Comments Policy here.