The Afro Latino who redefined how Black history is remembered
Share
Explore Our Galleries
Breaking News!
Today's news and culture by Black and other reporters in the Black and mainstream media.
Ways to Support ABHM?
By Nicole Acevedo, NBC News
Arturo Schomburg’s experiences as an Afro Puerto Rican at the turn of the century influenced his approach to rescuing and preserving Black history.

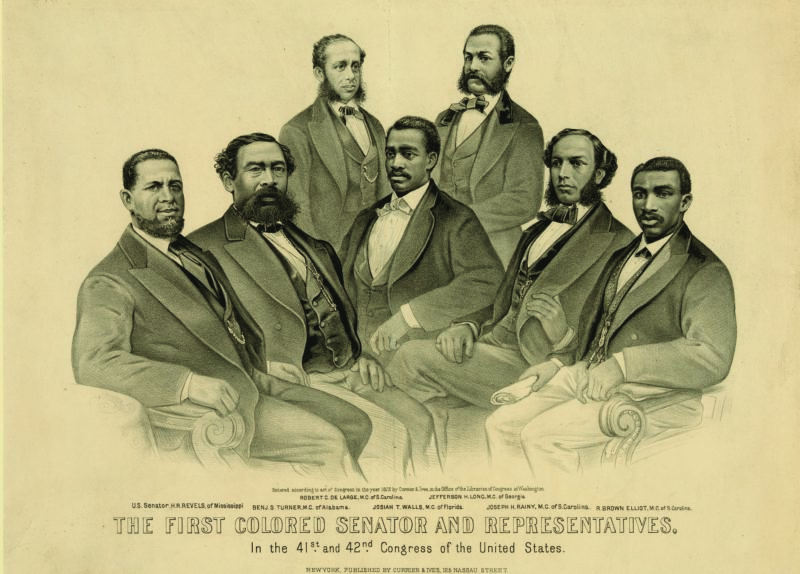
Arturo Alfonso Schomburg is regarded as one of the foundational figures of Black history in the United States, with one of the nation’s most important research and cultural institutions named after him.
Yet his legacy goes beyond the work he did as a historian, writer and collector of global Black art and historical materials.
By identifying as a Black and Puerto Rican, Schomburg’s acknowledgment of his diverse heritage helped him earn a global understanding of Black identity — a view he implemented in his approach to rescuing and preserving Black history — while he recognized the way Blackness had been erased, including in the Caribbean and Latin America.
To a certain extent, “this is what we still see happening,” said scholar Vanessa K. Valdés, as the erasing of Blackness and Black history remains an ongoing issue when retelling U.S., Caribbean and Latin American history. It’s a concern many Latinos, particularly from younger generations, are looking to address.
Born in Puerto Rico in 1874, the son of a Black mother from the Danish West Indies and a father of German descent, Schomburg noted that he grew up not knowing that the most famous 18th-century Puerto Rican painter, José Campeche, was Afro Puerto Rican like him.
Take a look into Schomburg’s efforts to preserve Black history.
Read the words of Black elders who know how important it is to continue saving history
More breaking news here.










Comments Are Welcome
Note: We moderate submissions in order to create a space for meaningful dialogue, a space where museum visitors – adults and youth –– can exchange informed, thoughtful, and relevant comments that add value to our exhibits.
Racial slurs, personal attacks, obscenity, profanity, and SHOUTING do not meet the above standard. Such comments are posted in the exhibit Hateful Speech. Commercial promotions, impersonations, and incoherent comments likewise fail to meet our goals, so will not be posted. Submissions longer than 120 words will be shortened.
See our full Comments Policy here.